- frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
1 概述
上篇Zygote经过RuntimeInit最后跳转到SystemServer的main方法,实现了 system_server进程 的初步分析,接下来我们从SystemServer的main()开始分析system_server进程。
2 SystemServer启动
2.1 SystemServer.main
[->SystemServer.java]
/**
* The main entry point from zygote.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
接下来看下run()方法。
2.2 SystemServer.run
private void run() {
try {
//当系统时间比1970年更早,就设置当前系统时间为1970年
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME) {
Slog.w(TAG, "System clock is before 1970; setting to 1970.");
SystemClock.setCurrentTimeMillis(EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME);
}
//设置时区
String timezoneProperty = SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.timezone");
if (timezoneProperty == null || timezoneProperty.isEmpty()) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Timezone not set; setting to GMT.");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.timezone", "GMT");
}
//设置系统的语言环境等
if (!SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.language").isEmpty()) {
final String languageTag = Locale.getDefault().toLanguageTag();
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale", languageTag);
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.country", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.localevar", "");
}
// The system server should never make non-oneway calls
Binder.setWarnOnBlocking(true);
// Here we go!
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
int uptimeMillis = (int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_SYSTEM_RUN, uptimeMillis);
if (!mRuntimeRestart) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_system_server_init", uptimeMillis);
}
//变更虚拟机的库文件
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2", VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmLibrary());
//清除vm内存增长上限,由于启动过程需要较多的虚拟机内存空间
VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
// The system server has to run all of the time, so it needs to be
// as efficient as possible with its memory usage.
//设置内存的可能有效使用率为0.8
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
// Some devices rely on runtime fingerprint generation, so make sure
// we've defined it before booting further.
Build.ensureFingerprintProperty();
// Within the system server, it is an error to access Environment paths without
// explicitly specifying a user.
//访问环境变量前,需要明确地指定用户
Environment.setUserRequired(true);
// Within the system server, any incoming Bundles should be defused
// to avoid throwing BadParcelableException.
BaseBundle.setShouldDefuse(true);
// Ensure binder calls into the system always run at foreground priority.
//确保当前系统进程的binder调用,总是运行在前台优先级(foreground priority)
BinderInternal.disableBackgroundScheduling(true);
// Increase the number of binder threads in system_server
BinderInternal.setMaxThreads(sMaxBinderThreads);
// Prepare the main looper thread (this thread).
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground(false);
// 主线程looper就在当前线程运行
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// Initialize native services.
//加载android_servers.so库,该库包含的源码在frameworks/base/services/目录下
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
// Check whether we failed to shut down last time we tried.
// This call may not return.
//检测上次关机过程是否失败,该方法可能不会返回
performPendingShutdown();
// Initialize the system context.
//初始化系统上下文
createSystemContext();
// Create the system service manager.
//创建系统服务管理
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
mSystemServiceManager.setRuntimeRestarted(mRuntimeRestart);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Prepare the thread pool for init tasks that can be parallelized
SystemServerInitThreadPool.get();
} finally {
traceEnd(); // InitBeforeStartServices
}
// Start services.
try {
traceBeginAndSlog("StartServices");
//启动各种系统服务
startBootstrapServices();
startCoreServices();
startOtherServices();
SystemServerInitThreadPool.shutdown();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
traceEnd();
}
// For debug builds, log event loop stalls to dropbox for analysis.
//用于debug版本,将log事件不断循环地输出到dropbox(用于分析)
if (StrictMode.conditionallyEnableDebugLogging()) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Enabled StrictMode for system server main thread.");
}
if (!mRuntimeRestart && !isFirstBootOrUpgrade()) {
int uptimeMillis = (int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_system_server_ready", uptimeMillis);
final int MAX_UPTIME_MILLIS = 60 * 1000;
if (uptimeMillis > MAX_UPTIME_MILLIS) {
Slog.wtf(SYSTEM_SERVER_TIMING_TAG,
"SystemServer init took too long. uptimeMillis=" + uptimeMillis);
}
}
// Loop forever.
//一直循环执行
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
通过SystemServiceManager的构造方法创建了一个新的SystemServiceManager对象,我们知道SystemServer进程主要是用来构建系统各种service服务的,而SystemServiceManager就是这些服务的管理对象。 接着调用下面三个与服务相关的方法:
-
startBootstrapServices() 主要用于启动系统Boot级服务
-
startCoreServices() 主要用于启动系统核心的服务
-
startOtherServices() 主要用于启动一些非紧要或者是非需要及时启动的服务
下面我们重点介绍这三个启动服务的方法,包括启动那些系统服务已经如何启动系统服务等。
2.2.1 createSystemContext
[–>SystemServer.java]
private void createSystemContext() {
ActivityThread activityThread = ActivityThread.systemMain();
//创建system_server进程的上下文信息
mSystemContext = activityThread.getSystemContext();
mSystemContext.setTheme(DEFAULT_SYSTEM_THEME);
final Context systemUiContext = activityThread.getSystemUiContext();
//设置主题
systemUiContext.setTheme(DEFAULT_SYSTEM_THEME);
}
该过程会创建对象有ActivityThread,Instrumentation, ContextImpl,LoadedApk,Application。通过ActivityThread.java来操作,和启动一个应用进程类似,只不过应用进程是使用ActivityThread.java->main(),这里是使用ActivityThread.java->systemMain()。这两者一定有区别,因为普通进程是要attach到AMS的,这里AMS还没有创建,不展开分析。
2.2.2 startBootstrapServices
private void startBootstrapServices() {
...
//阻塞等待与installd建立socket通道
//Installer提供安装、卸载App等服务
Installer installer = mSystemServiceManager.startService(Installer.class);
traceEnd();
...
//启动服务ActivityManagerService,提供Activity等组件的管理的服务
// Activity manager runs the show.
traceBeginAndSlog("StartActivityManager");
mActivityManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
traceEnd();
//启动服务PowerManagerService,管理电源相关的服务
// Power manager needs to be started early because other services need it.
// Native daemons may be watching for it to be registered so it must be ready
// to handle incoming binder calls immediately (including being able to verify
// the permissions for those calls).
traceBeginAndSlog("StartPowerManager");
mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class);
traceEnd();
// Now that the power manager has been started, let the activity manager
// initialize power management features.
traceBeginAndSlog("InitPowerManagement");
//初始化power management
mActivityManagerService.initPowerManagement();
traceEnd();
// Bring up recovery system in case a rescue party needs a reboot
if (!SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.disable_noncore", false)) {
traceBeginAndSlog("StartRecoverySystemService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(RecoverySystemService.class);
traceEnd();
}
// Now that we have the bare essentials of the OS up and running, take
// note that we just booted, which might send out a rescue party if
// we're stuck in a runtime restart loop.
RescueParty.noteBoot(mSystemContext);
// Manages LEDs and display backlight so we need it to bring up the display.
traceBeginAndSlog("StartLightsService");
//启动服务LightsService,LED管理和背光显示的服务
mSystemServiceManager.startService(LightsService.class);
traceEnd();
// Display manager is needed to provide display metrics before package manager
// starts up.
traceBeginAndSlog("StartDisplayManager");
//启动服务DisplayManagerService
//提供显示的生命周期管理,根据物理显示设备当前的情况决定显示配置,在状态改变时发送通知给系统和应用等服务
mDisplayManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(DisplayManagerService.class);
traceEnd();
// We need the default display before we can initialize the package manager.
traceBeginAndSlog("WaitForDisplay");
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(SystemService.PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
traceEnd();
//当设备正在加密时,仅运行核心
// Only run "core" apps if we're encrypting the device.
String cryptState = SystemProperties.get("vold.decrypt");
if (ENCRYPTING_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Detected encryption in progress - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
} else if (ENCRYPTED_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Device encrypted - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
}
if (RegionalizationEnvironment.isSupported()) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Regionalization Service");
RegionalizationService regionalizationService = new RegionalizationService();
ServiceManager.addService("regionalization", regionalizationService);
}
// Start the package manager.
if (!mRuntimeRestart) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_package_manager_init_start",
(int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
}
traceBeginAndSlog("StartPackageManagerService");
//启动服务PackageManagerService,该服务用于管理所有的.apk
mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main(mSystemContext, installer,
mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF, mOnlyCore);
mFirstBoot = mPackageManagerService.isFirstBoot();
mPackageManager = mSystemContext.getPackageManager();
traceEnd();
if (!mRuntimeRestart && !isFirstBootOrUpgrade()) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_package_manager_init_ready",
(int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
}
// Manages A/B OTA dexopting. This is a bootstrap service as we need it to rename
// A/B artifacts after boot, before anything else might touch/need them.
// Note: this isn't needed during decryption (we don't have /data anyways).
if (!mOnlyCore) {
boolean disableOtaDexopt = SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.disable_otadexopt",
false);
if (!disableOtaDexopt) {
traceBeginAndSlog("StartOtaDexOptService");
try {
OtaDexoptService.main(mSystemContext, mPackageManagerService);
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("starting OtaDexOptService", e);
} finally {
traceEnd();
}
}
}
//启动服务UserManagerService,新建目录/data/user/,提供用户相关服务
traceBeginAndSlog("StartUserManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UserManagerService.LifeCycle.class);
traceEnd();
// Initialize attribute cache used to cache resources from packages.
traceBeginAndSlog("InitAttributerCache");
AttributeCache.init(mSystemContext);
traceEnd();
//设置AMS
// Set up the Application instance for the system process and get started.
traceBeginAndSlog("SetSystemProcess");
mActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
traceEnd();
// DisplayManagerService needs to setup android.display scheduling related policies
// since setSystemProcess() would have overridden policies due to setProcessGroup
mDisplayManagerService.setupSchedulerPolicies();
// Manages Overlay packages
traceBeginAndSlog("StartOverlayManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(new OverlayManagerService(mSystemContext, installer));
traceEnd();
// The sensor service needs access to package manager service, app ops
// service, and permissions service, therefore we start it after them.
// Start sensor service in a separate thread. Completion should be checked
// before using it.
mSensorServiceStart = SystemServerInitThreadPool.get().submit(() -> {
TimingsTraceLog traceLog = new TimingsTraceLog(
SYSTEM_SERVER_TIMING_ASYNC_TAG, Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
traceLog.traceBegin(START_SENSOR_SERVICE);
//启动传感器服务
startSensorService();
traceLog.traceEnd();
}, START_SENSOR_SERVICE);
}
该方法所创建的服务:ActivityManagerService, PowerManagerService, LightsService, DisplayManagerService, PackageManagerService, UserManagerService, sensor服务.
2.2.3 startCoreServices
private void startCoreServices() {
// Records errors and logs, for example wtf()
traceBeginAndSlog("StartDropBoxManager");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(DropBoxManagerService.class);
traceEnd();
//启动服务BatteryService,用于统计电池电量
traceBeginAndSlog("StartBatteryService");
// Tracks the battery level. Requires LightService.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BatteryService.class);
traceEnd();
//启动服务UsageStatsService,用于统计应用使用情况
// Tracks application usage stats.
traceBeginAndSlog("StartUsageService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UsageStatsService.class);
mActivityManagerService.setUsageStatsManager(
LocalServices.getService(UsageStatsManagerInternal.class));
traceEnd();
// Tracks whether the updatable WebView is in a ready state and watches for update installs.
//启动服务WebViewUpdateService
traceBeginAndSlog("StartWebViewUpdateService");
mWebViewUpdateService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(WebViewUpdateService.class);
traceEnd();
}
启动服务BatteryService,UsageStatsService,WebViewUpdateService。
2.2.4 startOtherServices
该方法主要用于启动系统中其他的服务,代码很多,这里就不贴代码了,启动的流程和ActivityManagerService的流程类似,会调用服务的构造方法与onStart方法初始化变量。
到此, System_server主线程的启动工作总算完成, 进入Looper.loop()状态,等待其他线程通过handler发送消息到主线再处理.
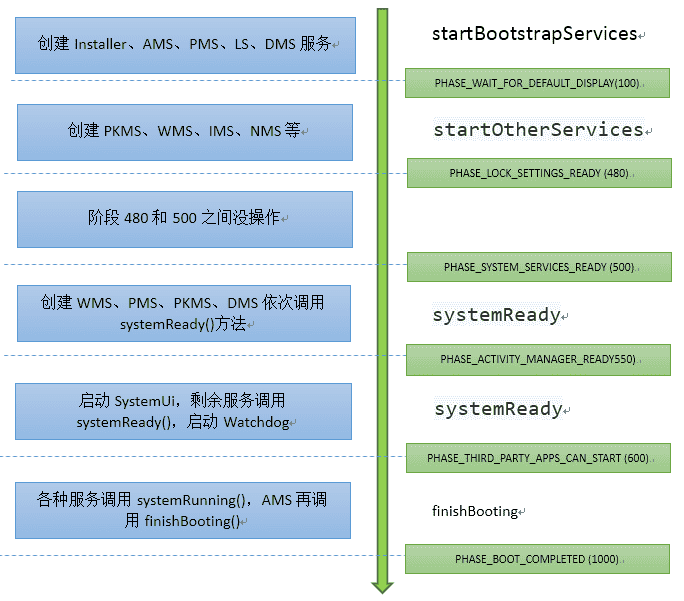
3 服务启动阶段
SystemServiceManager的startBootPhase()贯穿system_server进程的整个启动过程:
/*
* Boot Phases
*/
public static final int PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY = 100; // maybe should be a dependency?
/**
* After receiving this boot phase, services can obtain lock settings data.
*/
public static final int PHASE_LOCK_SETTINGS_READY = 480;
/**
* After receiving this boot phase, services can safely call into core system services
* such as the PowerManager or PackageManager.
*/
public static final int PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY = 500;
/**
* After receiving this boot phase, services can broadcast Intents.
*/
public static final int PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY = 550;
/**
* After receiving this boot phase, services can start/bind to third party apps.
* Apps will be able to make Binder calls into services at this point.
*/
public static final int PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START = 600;
/**
* After receiving this boot phase, services can allow user interaction with the device.
* This phase occurs when boot has completed and the home application has started.
* System services may prefer to listen to this phase rather than registering a
* broadcast receiver for ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED to reduce overall latency.
*/
public static final int PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED = 1000;
启动流程分析:
- PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY=100,该阶段等待Display有默认显示;
- PHASE_LOCK_SETTINGS_READY=480,进入该阶段服务能获取锁屏设置的数据;
- PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY=500,进入该阶段服务能安全地调用核心系统服务,如PMS;
- PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY=550,进入该阶段服务能广播Intent;
- PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START=600,进入该阶段服务能start/bind第三方apps,app能通过BInder调用service;
- PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED=1000,该阶段是发生在Boot完成和home应用启动完毕。系统服务更倾向于监听该阶段,而不是注册广播ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED,从而降低系统延迟。
接下来再说说简单每个阶段的大概完成的工作。
3.1 Phase100
创建ActivityManagerService、PowerManagerService、LightsService、DisplayManagerService共4项服务;
接着则进入阶段100,该阶段调用DisplayManagerService的onBootPhase()方法。
3.2 Phase 480&&500
创建PackageManagerService、WindowManagerService、InputManagerService、NetworkManagerService、DropBoxManagerService/FingerprintService等服务
接着则进入阶段480,该阶段调用DevicePolicyManagerService的onBootPhase()方法; 紧接着进入阶段500,实现该阶段的回调方法的服务较多。
3.3 Phase 550
WindowManagerService、PowerManagerService、PackageManagerService、DisplayManagerService分别依次执行systemReady()方法;然后ActivityManagerService进入systemReady()方法;
接着则进入阶段550,实现该阶段的回调方法的服务较多。
3.4 Phase 600
AMS启动native crash监控,,加载WebView,启动SystemUi;然后是NetworkScoreService、NetworkManagementService、NetworkStatsService、NetworkPolicyManagerService、ConnectivityService、AudiOService分别依次执行systemReady()方法,然后是启动Watchdog。
接着则进入阶段600,实现该阶段的回调方法的服务较多。
3.5 Phase 1000
WallpaperManagerService、InputMethodManagerService、LocationManagerService、CountryDetectorService、NetworkTimeUpdateService、CommonTimeManagementService、TextServicesManagerService、AssetAtlasService、InputManagerService、TelephonyRegistry、MediaRouterService、MmsServiceBroker这些服务依次执行其systemRunning()方法。经过一定流程,当ActivityManagerServer进入finishBooting()时,则启动流程进入阶段PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED=1000。
到此所有服务启动完成,system_server进程启动完成,则进入Looper.loop()状态,随时待命,等待MessageQueue中的消息到来,则马上进入执行状态。
4 服务类型
system_server进程,从源码角度划分为引导服务、核心服务、其他服务3类,合计总大约80多个服务,下面只是简单地对所有服务分类(个人划分,便于后期分析):

后续,会针对其中比较重要的服务进行展开详解。